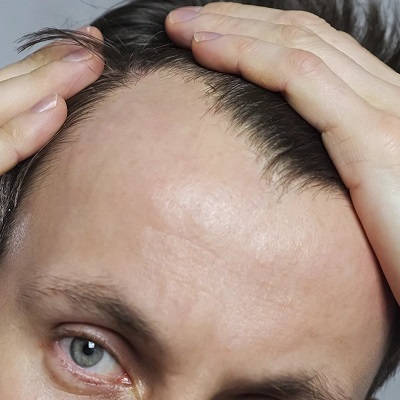
Hair is often referred to as a person’s crowning glory, so experiencing excessive hair shedding can be distressing and concerning. While it’s normal to lose some hair daily—about 50 to 100 strands—seeing more than that can raise alarms. Understanding the various factors that contribute to hair shedding is crucial for addressing the issue effectively. This blog will delve into the potential causes of excessive hair shedding, how it occurs, and what steps can be taken to manage and reverse it.
Understanding Hair Shedding:
To grasp why excessive hair shedding occurs, it helps to understand the hair growth cycle. Hair goes through three main phases:
- Anagen Phase: This is the active growth phase, lasting 2 to 7 years. During this time, hair grows continuously, with healthy strands emerging from the scalp.
- Catagen Phase: This transitional phase lasts about 2 to 3 weeks, during which hair growth slows, and the hair follicle begins to shrink.
- Telogen Phase: This resting phase lasts approximately 3 months. At this point, hair is shed, and new hair begins to grow in its place.
When a larger number of hair follicles enter the telogen phase simultaneously, it results in excessive shedding, which can be alarming.
Common Causes of Excessive Hair Shedding:
1. Genetics and Heredity:
One of the leading causes of hair shedding is genetic predisposition. Conditions such as androgenetic alopecia, often referred to as male or female pattern baldness, can lead to gradual thinning and excessive shedding over time. If you have a family history of hair loss, you may be at a higher risk of experiencing similar issues.
2. Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations can have a significant impact on hair health. Events such as pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, and hormonal disorders like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to changes in hormone levels that trigger hair shedding. For instance, many women experience telogen effluvium—a temporary form of hair loss—after giving birth due to hormonal shifts.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies:
A well-balanced diet is essential for maintaining healthy hair. Deficiencies in vital nutrients such as iron, zinc, biotin, and vitamins A and D can result in weakened hair follicles and increased shedding. If your diet lacks these essential nutrients, your hair may suffer.
4. Stress and Emotional Well-Being:
Stress plays a significant role in hair shedding. Both physical and emotional stress can push hair follicles into the telogen phase prematurely. Events like a traumatic experience, loss, or even significant life changes can result in noticeable shedding. Chronic stress can exacerbate this issue, leading to conditions like telogen effluvium, where hair falls out in larger clumps.
5. Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions can contribute to hair shedding. Autoimmune disorders, such as alopecia areata, occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, resulting in patchy hair loss in Islamabad. Additionally, thyroid disorders, scalp infections, and chronic illnesses can also lead to increased shedding.
6. Medications:
Several medications have hair loss as a potential side effect. Common examples include blood thinners, antidepressants, and medications used to treat cancer. If you have recently started a new medication and noticed increased hair shedding, it’s essential to consult your healthcare provider to discuss your concerns.
7. Hairstyling Practices:
Frequent hairstyling that puts stress on hair strands can lead to a condition called traction alopecia. Tight hairstyles such as ponytails, braids, or extensions can pull on the hair and cause it to shed. Additionally, the excessive use of heat styling tools and harsh chemical treatments can weaken hair, leading to breakage and shedding.
What to Do About Excessive Hair Shedding:
1. Consult a Healthcare Professional:
If you’re concerned about excessive hair shedding, the first step is to consult a dermatologist or trichologist. They can perform tests to identify the underlying cause of your hair loss and recommend appropriate treatments.
2. Improve Your Diet:
Focus on maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals essential for hair health. Incorporate foods high in iron (such as spinach and legumes), zinc (like nuts and seeds), and protein (found in lean meats, fish, and dairy) to support hair growth.
3. Manage Stress:
Engaging in stress-reducing activities can help alleviate hair shedding. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can contribute to overall well-being and reduce stress levels.
4. Avoid Harsh Hair Treatments:
Be mindful of the products and treatments you use on your hair. Opt for gentle shampoos and conditioners free from sulfates and parabens, and minimize the use of heat styling tools. Avoid hairstyles that pull tightly on the hair to reduce the risk of traction alopecia.
5. Consider Supplements:
If you suspect nutritional deficiencies, consider discussing dietary supplements with your healthcare provider. Biotin, zinc, and iron supplements may help promote hair health and reduce shedding.
6. Explore Medical Treatments:
Depending on the underlying cause of your hair shedding, various treatments may be available. Options include topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, or even platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. Your healthcare provider can help you explore the most suitable options for your situation.
Conclusion:
Experiencing excessive hair shedding can be a worrying experience, but understanding the potential causes can help you take proactive steps to manage the issue. From genetic predispositions to stress and nutritional deficiencies, various factors can contribute to hair shedding. If you’re facing this concern, seeking professional advice is vital to finding an effective solution. With the right approach and support, you can work toward healthier hair and renewed confidence.
For more information visit Dynamic Clinic PK