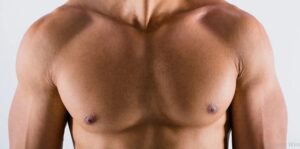
Gynecomastia is a condition that affects a significant number of men worldwide, causing physical and emotional distress. While it may not always be openly discussed, male breast enlargement is more common than many realize. It can occur at various stages of life, from infancy and adolescence to older adulthood. Although it’s usually not a serious health issue, it can impact self-esteem, body image, and overall confidence. In this article, we’ll explore what gynecomastia is, what causes it, how it presents itself, and the most effective treatment options available today. This guide aims to provide clarity for those affected and support for individuals seeking a better understanding of the condition.
In the center of this growing concern lies a need for greater awareness and accurate information surrounding gynecomastia male breast issues that affect both physical appearance and emotional well-being.
What Is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia refers to the benign enlargement of breast glandular tissue in males. It’s different from simply having excess chest fat, which is known as pseudogynecomastia. True gynecomastia involves an actual increase in glandular breast tissue rather than fat accumulation. This condition can affect one or both breasts, sometimes unevenly, and is often noticed as a small lump or swelling beneath the nipple area. While it’s typically painless, some individuals may experience tenderness or sensitivity.
Hormonal imbalances are the primary underlying cause. Specifically, when the balance between estrogen (the hormone responsible for female characteristics) and testosterone (the male hormone) shifts, even slightly, breast tissue may begin to grow. This imbalance can be due to natural body changes, medical conditions, or external influences like medications and substance use.
Common Causes Behind Male Breast Enlargement
Gynecomastia may arise from various causes, making diagnosis and treatment a bit complex without proper medical evaluation. One of the most common causes is hormonal fluctuation during puberty. Many teenage boys experience temporary gynecomastia that typically resolves on its own within a year or two. Similarly, older men may experience it as testosterone levels naturally decline with age.
Certain medications can also play a major role. Drugs used for treating ulcers, heart conditions, cancer, and psychiatric disorders sometimes trigger breast tissue growth as a side effect. Additionally, anabolic steroids, commonly used by athletes and bodybuilders to enhance muscle mass, are strongly linked to the development of gynecomastia.
Chronic illnesses like liver disease, kidney failure, and thyroid disorders can also lead to hormonal imbalances that cause this condition. In rare cases, tumors of the testes or adrenal glands may contribute to excess estrogen production. Substance abuse—including alcohol, marijuana, heroin, and amphetamines—has also been implicated in some instances of male breast enlargement.
Identifying the Symptoms and When to See a Doctor
The most noticeable symptom of gynecomastia is swelling or enlargement of the breast tissue. This growth is typically symmetrical and centered under the nipple, though it may occur on just one side. Some men experience sensitivity or pain, especially during the early stages. The tissue may feel firm or rubbery to the touch.
It’s important to differentiate between gynecomastia and other conditions, such as fat deposits in overweight individuals or more serious concerns like male breast cancer. While cancer in men is rare, it’s crucial to see a healthcare professional if there are signs like rapid growth, hard or irregular lumps, nipple discharge, or skin dimpling.
If gynecomastia persists for more than a few months, causes physical discomfort, or leads to emotional distress, medical consultation is recommended. A doctor may conduct a physical exam, review your medical history, and order tests such as blood work, hormone level checks, or imaging studies to determine the cause.
Treatment Options: From Lifestyle Changes to Surgery
Treatment for gynecomastia depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and the individual’s preferences. In many cases, especially when hormonal changes are temporary—such as during puberty—no treatment is necessary. The condition often resolves on its own within six months to two years.
When gynecomastia is linked to medication or substance use, simply stopping the triggering agent may lead to improvement. If a hormone imbalance is to blame, doctors might prescribe medication such as tamoxifen or raloxifene, which are selective estrogen receptor modulators. These drugs can help shrink breast tissue and alleviate discomfort, though they aren’t approved by the FDA specifically for gynecomastia and are typically reserved for moderate to severe cases.
For individuals who experience persistent or severe gynecomastia that does not respond to medical therapy, surgery may be the best option. The two primary surgical procedures include liposuction (to remove excess fat) and mastectomy (to remove glandular tissue). Modern surgical techniques are generally safe, minimally invasive, and produce natural-looking results with minimal scarring.
Lifestyle modifications also play a crucial role. Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding recreational drugs and anabolic steroids, and managing chronic medical conditions can all reduce the risk of developing or worsening gynecomastia. In cases where weight is a contributing factor, targeted exercise and proper nutrition may help improve chest contour, although they cannot eliminate glandular tissue.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
Beyond the physical aspects, gynecomastia can deeply affect a man’s emotional and psychological health. Body image issues, embarrassment, and social anxiety are common, particularly in adolescents and young adults. The condition may lead to avoidance of activities like swimming, going shirtless, or engaging in intimate relationships due to feelings of shame or insecurity.
Support groups, therapy, and open conversations with healthcare providers can help alleviate some of this emotional burden. When appropriate, medical or surgical treatment can provide not only physical relief but also a significant boost in confidence and quality of life. Understanding that gynecomastia is a medical condition—not a reflection of one’s masculinity or lifestyle choices—is key to overcoming its psychological effects.
Final Thoughts
Gynecomastia is a condition that many men silently endure, but it doesn’t have to be that way. By understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring available treatments, individuals can take informed steps toward recovery. While not always serious from a health perspective, male breast enlargement can significantly affect mental and emotional well-being. The good news is that effective solutions exist—from medication and lifestyle adjustments to surgical intervention. If you or someone you know is dealing with this condition, seeking medical advice is the first step toward regaining control and confidence.