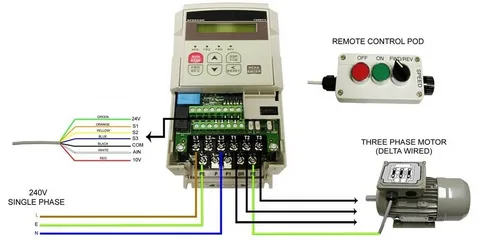
Inverters are vital in contemporary electrical systems, bridging the gap between direct (DC) sources and alternating (AC) power outputs. With the rising demand for efficient energy solutions, comprehending the differences between various inverter types, such as single-phase and Three Phase Inverter, is increasingly important. Each type of inverter serves distinct applications, from residential to industrial settings. By converting DC to AC, inverters enable the functioning of everyday appliances and complex machinery. This exploration will provide insights into both single-phase and three-phase inverters’ structures, applications, and benefits, highlighting their relevance in modern energy management.
Understanding Single-Phase Inverters
Single-phase inverters are designed to convert DC power into AC power with a single-phase output, primarily for residential applications. They efficiently support the operation of common household appliances, lighting, and small electronic devices. These inverters are straightforward in design, making them relatively easy to install and maintain. Their simplicity translates into lower initial costs and less technical complexity, which appeals to homeowners seeking reliable energy solutions.
Additionally, single-phase inverters can be integrated into renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, to enhance energy efficiency and reduce dependency on traditional power sources. Their role in ensuring a steady power supply for everyday use makes them a practical choice in domestic settings.
Exploring Three-Phase Inverters
Three-phase inverters are distinguished by their ability to convert DC power into a three-phase AC output, accommodating larger and more complex electrical loads. This makes them particularly suitable for industrial environments with heavy machinery and intricate systems demanding a stable and substantial power supply. Their design includes three separate AC outputs, distributing the electrical load evenly, thereby reducing energy losses and improving efficiency.
The robust nature of three-phase inverters enables them to support continuous and uninterrupted power delivery, which is essential for maintaining high productivity levels in industrial operations. Additionally, the balanced power distribution helps to mitigate electrical disturbances, ensuring the smooth functioning of sensitive equipment.
Advantages of a Single Phase Inverter
Single Phase Inverter is advantageous in residential environments due to their affordability and simplicity. Their straightforward design allows for easier installation and minimal technical expertise, which is highly beneficial for homeowners. Additionally, these inverters are well-suited for integrating with renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, enhancing energy efficiency in household settings.
The lower initial costs associated with single-phase inverters make them an economical choice, and their reliability ensures a consistent power supply for everyday electrical needs. Furthermore, their compact size and user-friendly operation contribute to their widespread adoption in domestic applications, where space and ease of use are paramount considerations.
Benefits of Three-Phase Inverters
Three-phase inverters deliver stable and continuous power, essential for maintaining productivity in industrial environments. Their design allows for balanced power distribution across three phases, significantly reducing the risk of electrical disturbances and energy losses. This efficiency translates into cost savings and enhanced operational performance. Additionally, three-phase inverters support high-capacity loads, making them ideal for running heavy machinery and intricate systems.
Their ability to minimise downtime through consistent power delivery is invaluable for industries relying on uninterrupted operations. Moreover, these inverters offer greater scalability, allowing businesses to expand their power infrastructure as needed without compromising on efficiency or reliability.
Transition from Single-Phase to Three-Phase Inverters
Transitioning from a single-phase to a three-phase inverter system necessitates strategic planning and careful execution. This process is often driven by the need to support larger electrical loads and enhance operational efficiency. The first step involves evaluating the existing electrical infrastructure to determine compatibility with three-phase systems. Upgrading the wiring and distribution network may be required to handle the increased power capacity.
Additionally, selecting the appropriate inverter converter is crucial for ensuring seamless integration between the existing single-phase setup and the new three-phase equipment. This upgrade can significantly enhance energy distribution and reduce power losses, improving overall system performance. Proper installation and calibration of the new three-phase inverter are essential for optimal functionality.
Skilled technicians typically handle this transition to ensure compliance with safety standards and to mitigate potential issues. By adopting a three-phase system, businesses can benefit from more efficient energy use and greater reliability in their operations, accommodating future expansion and technological advancements.
Components of a Three-Phase Inverter
A three-phase inverter comprises several crucial components facilitating the conversion process from DC to AC. Central to its design are power switches, which handle the rapid switching necessary for generating AC output. Control circuitry ensures precise timing and modulation, optimising the performance and stability of the inverter. An input source provides the initial DC power, while an output filter smooths the converted AC to make it suitable for use with industrial equipment.
Additional components include cooling mechanisms to manage heat dissipation and protective devices to safeguard against electrical faults. These elements work in concert to ensure the three-phase inverter operates efficiently and reliably in demanding industrial environments.
Single Phase to 3 Phase Inverter Converters
Single Phase to 3 Phase Inverter converters are essential in applications where single-phase power systems must support three-phase equipment. These converters work by splitting the single-phase input into a three-phase output, thereby enabling the use of more robust and efficient machinery. Typically found in environments undergoing upgrades or expansions, these devices facilitate a smooth transition by ensuring compatibility between existing single-phase systems and new three-phase requirements.
This conversion process enhances operational efficiency and allows for greater flexibility in power distribution. By accommodating the increased electrical demands, single-phase to three-phase inverter converters are crucial in modernising and optimising electrical infrastructure.
Installation Considerations for Inverters
Proper installation of inverters is critical for achieving optimal performance and longevity. It is essential to assess the electrical load requirements and ensure that the inverter capacity aligns with these demands. Adequate ventilation must be provided to prevent overheating, which can compromise the inverter’s efficiency and lifespan. The installation site should be free from excessive dust and moisture to avoid damage to the internal components. Proper grounding and surge protectors safeguard the inverter from electrical faults and transient voltage spikes.
Compatibility with existing electrical systems is necessary to avoid disruptions and ensure smooth integration. Skilled technicians should handle the installation process, adhering to safety standards and manufacturer guidelines. Regular monitoring and maintenance are recommended post-installation to address any potential issues promptly. Ensuring these considerations can significantly enhance the reliability and performance of both single-phase and three-phase inverters, catering to the specific needs of residential or industrial applications.
Maintenance of Single and Three-Phase Inverters
The provided text emphasizes the importance of regular maintenance for both single-phase and three-phase inverters to ensure their efficient and prolonged operation. It outlines several key maintenance activities that contribute to the reliability and longevity of these devices.
Inspecting Connections and Ventilation
Regular inspections of electrical connections are crucial to ensure they remain secure and free from corrosion. Simultaneously, checking ventilation systems helps prevent overheating, a common cause of inverter failure. Proper airflow is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
Cleaning Filters and Fans
Periodic cleaning of filters and fans is necessary to maintain optimal airflow. Dust and debris accumulation can obstruct airflow, leading to increased operating temperatures and reduced efficiency. Regular cleaning helps prevent these issues.
Testing Electrical Parameters
Testing electrical parameters such as voltage, current, and waveform quality is vital for identifying potential issues before they escalate. Regular testing can help detect deviations from normal operating conditions, allowing for timely intervention.
Monitoring for Unusual Noises or Vibrations
Monitoring for unusual noises or vibrations can signal underlying mechanical problems. Early detection of these issues can prevent more significant damage and costly repairs.
Replacing Worn Components and Updating Firmware
Promptly replacing worn-out components and updating firmware as recommended by manufacturers are essential maintenance practices. These actions ensure that the inverter operates at peak performance and benefits from the latest technological improvements.
Cost Implications of Inverter Types
Financial considerations are critical for residential and industrial users when selecting single-phase and three-phase inverters. Single-phase inverters generally offer a more budget-friendly option, appealing to homeowners due to their lower upfront costs and straightforward installation requirements. These inverters are particularly suited for applications with moderate electrical load and do not demand complex power distribution.
On the other hand, though involving higher initial investment, three-phase inverters provide substantial benefits for industrial settings. Their capability to efficiently handle large-scale power loads and reduce energy losses can result in long-term cost savings. The initial expenditure on three-phase inverters is offset by their enhanced performance and reliability to demanding applications. Thus, while the upfront costs may be higher, the improved efficiency and reduced operational disruptions present a compelling economic case for industries.
Future Trends in Inverter Technology
Future advancements in inverter technology are poised to revolutionise energy systems across various sectors. Emerging innovations include developing advanced semiconductor materials, which promise greater efficiency and durability. Enhanced control algorithms are designed to optimise performance, allowing for more precise energy management and reduced losses. Additionally, integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies is set to improve inverters’ predictive maintenance and adaptive capabilities, ensuring more reliable operations.
The rise of smart grid technology is also a significant trend, enabling inverters to communicate and interact with broader energy networks. This connectivity will facilitate more effective load balancing and energy distribution, contributing to overall grid stability and resilience. Moreover, the increasing focus on renewable energy sources drives the need for inverters that seamlessly integrate with solar panels, wind turbines, and other sustainable energy systems.
The push towards miniaturisation and enhanced cooling solutions will result in more compact and efficient inverter designs suitable for various applications. These trends collectively indicate a future where inverters meet the growing energy demands and support a more sustainable and efficient power infrastructure.
Conclusion
Single-phase and Three Phase Inverter serves distinct yet crucial roles in modern electrical systems. Single-phase inverters, with their simplicity and affordability, are ideal for residential applications, providing reliable power for everyday appliances. Conversely, three-phase inverters excel in industrial settings, delivering robust and stable power for heavy machinery and complex systems. The transition from single-phase to three-phase systems requires careful planning and execution, often driven by the need to support increased electrical loads and improve efficiency. Proper installation and maintenance are essential for both types, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. As technology advances, future inverters will feature enhanced control algorithms, smarter grid integration, and more compact designs, further driving efficiency and reliability. The choice between single-phase and three-phase inverters depends on the specific application’s requirements, with each offering unique advantages in its respective domain.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between single-phase and Three Phase Inverter?
Single-phase inverters deliver AC power for residential use, while Three Phase Inverter provides stable, high-capacity power for industrial applications.
Why are three-phase inverters preferred in industrial settings?
They offer balanced power distribution, reducing energy losses and supporting heavy machinery with stable, continuous power.
What are the key components of a three-phase inverter?
Power switches, control circuitry, input source, output filter, cooling mechanisms, and protective devices.
What factors should be considered during inverter installation?
Electrical load requirements, ventilation, grounding, compatibility with existing systems, and professional installation.
How does the cost differ between single-phase and three-phase inverters?
Single-phase inverters are generally more affordable for residential use, while three-phase inverters have higher upfront costs but offer long-term efficiency benefits in industrial settings.
| Related Business Listings |
| Contact Directory |
| Local Business Profiles |