Living with neuropathic pain can feel like an unending struggle, a sharp, burning, or electric-like sensation that affects your ability to work, rest, or simply enjoy daily life. Unlike typical pain caused by injury or inflammation, neuropathic pain stems from nerve damage or dysfunction in the nervous system. It’s chronic, complex, and often misunderstood, making accurate diagnosis and effective treatment essential.
We’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for neuropathic pain and how you can manage it for a better quality of life.
What Is Neuropathic Pain?
Neuropathic pain occurs when nerves responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and spinal cord malfunction. Instead of sending normal sensory signals, damaged nerves send incorrect or exaggerated pain signals to the brain even in the absence of injury.
This type of pain is often chronic and can persist long after the initial cause has healed. It can be localized (affecting one area) or widespread, depending on the extent of nerve involvement.
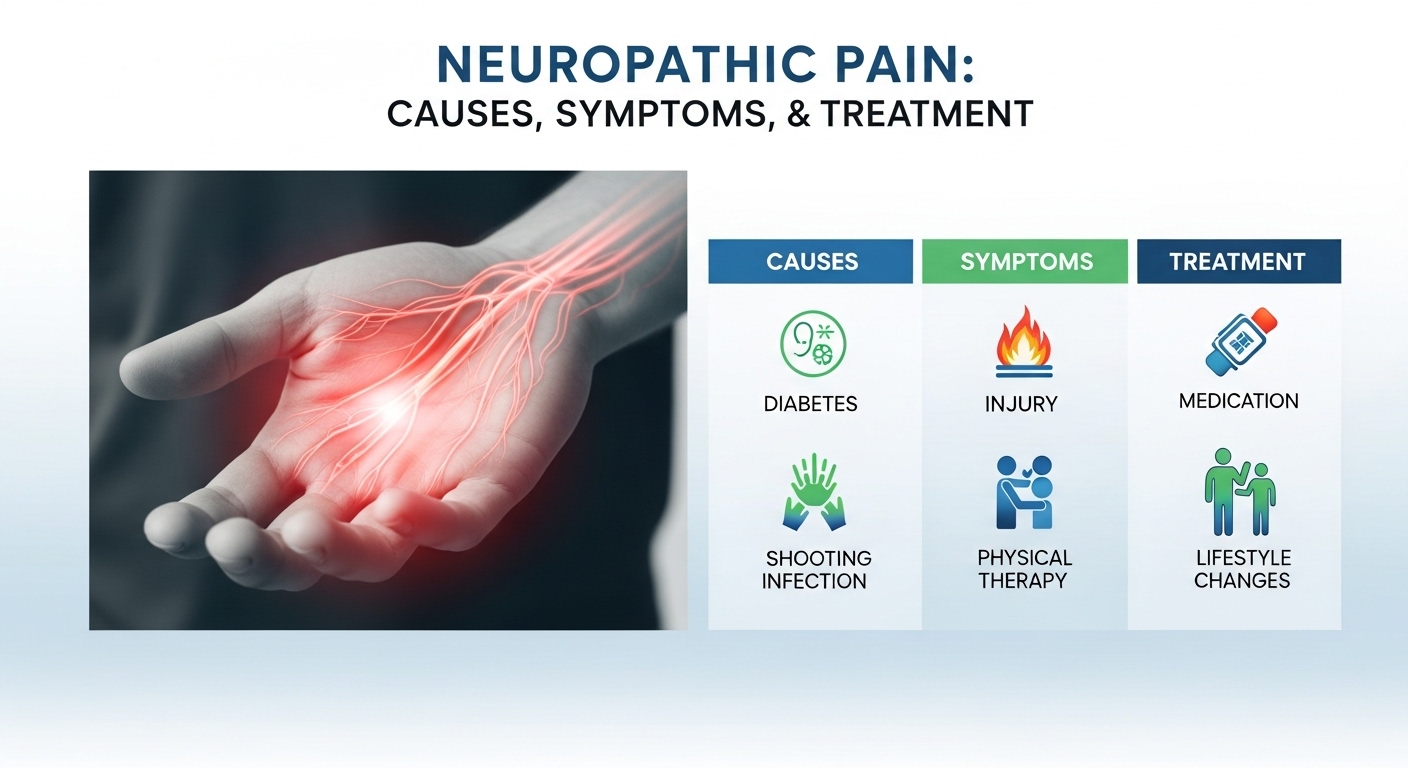
Common Causes of Neuropathic Pain
Neuropathic pain can develop due to various underlying health conditions or injuries. Some of the most common causes include:
1. Diabetes (Diabetic Neuropathy)
Diabetes is one of the leading causes of neuropathic pain. Over time, high blood sugar damages peripheral nerves, especially in the hands and feet, causing numbness, tingling, or sharp shooting pain.
2. Nerve Injuries
Trauma or compression of nerves such as from a herniated disc, car accident, or surgery can result in chronic neuropathic pain.
3. Infections
Conditions like shingles (postherpetic neuralgia) or HIV can cause inflammation and nerve damage, leading to persistent pain even after the infection resolves.
4. Autoimmune Disorders
Diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS) and lupus can attack nerve tissues, disrupting communication within the nervous system.
5. Cancer and Chemotherapy
Certain cancers or chemotherapy drugs can damage nerve endings, causing tingling or burning sensations.
Symptoms of Neuropathic Pain
The symptoms of neuropathic pain can vary from mild discomfort to severe, disabling sensations. Common symptoms include:
- Burning, stabbing, or electric-shock-like pain
- Increased sensitivity to touch or cold
- Numbness or tingling in the affected area
- Spontaneous pain without any apparent cause
- Muscle weakness or coordination problems
People often describe the pain as shooting or radiating, which can interfere with sleep, mood, and mobility. In some cases, the pain is constant; in others, it occurs in unpredictable bursts.
How Neuropathic Pain Affects the Body and Mind
Chronic neuropathic pain doesn’t just affect the nerves it impacts your emotional and mental well-being too. Persistent pain can lead to anxiety, depression, and fatigue, creating a cycle that makes the condition harder to manage. The nervous system becomes hypersensitive, and over time, even mild sensations may feel intensely painful, a process known as central sensitization.
Diagnosing Neuropathic Pain
Diagnosing neuropathic pain requires a detailed medical assessment. Healthcare professionals often use a combination of:
- Physical exams and medical history reviews
- Nerve conduction studies or electromyography (EMG)
- MRI scans to detect spinal or brain abnormalities
- Quantitative sensory testing (QST) to measure nerve sensitivity
An accurate diagnosis helps determine whether the pain is neuropathic or caused by another underlying condition.
Best Treatment Options for Neuropathic Pain
Treating neuropathic pain often requires a multimodal approach combining medications, therapy, and lifestyle modifications. While there’s no one-size-fits-all cure, effective management can greatly reduce pain and improve daily function.
1. Medications
- Antidepressants: Drugs like amitriptyline and duloxetine help calm overactive nerves and relieve pain.
- Anticonvulsants: Medications such as gabapentin and pregabalin stabilize nerve activity.
- Topical treatments: Lidocaine or capsaicin creams can provide localized relief.
- Pain relievers: In severe cases, opioids may be prescribed short-term under strict medical supervision.
2. Physical and Occupational Therapy
Physical therapy can help improve mobility, reduce stiffness, and enhance muscle strength. Techniques like TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) are often used to ease nerve discomfort.
3. Psychological Support
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based techniques help patients cope with the emotional burden of chronic pain. Managing stress can reduce flare ups and enhance pain tolerance.
4. Alternative and Natural Therapies
Some patients find relief with acupuncture, massage therapy, or CBD oil, which may help relax nerves and improve blood flow. These should always be used in consultation with a healthcare professional.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
- Maintain healthy blood sugar levels (for diabetics)
- Follow an anti-inflammatory diet
- Exercise regularly and get enough sleep
- Avoid alcohol and smoking, which can worsen nerve damage
FAQs About Neuropathic Pain
Q1: Can neuropathic pain go away completely?
In some cases, yes if the underlying cause is treated early. However, chronic nerve damage may require long-term management to control symptoms.
Q2: What is the most effective medication for neuropathic pain?
Antidepressants and anticonvulsants are often the first-line treatments, though effectiveness varies per individual.
Q3: How can I tell if my pain is neuropathic?
If your pain feels like burning, tingling, or electric shocks and occurs without injury it may be neuropathic. A doctor can confirm this through diagnostic tests.
Q4: Is exercise safe for neuropathic pain?
Yes, gentle exercise can improve circulation and reduce nerve sensitivity. Always start slowly and consult a physiotherapist if pain worsens.
Q5: Are there natural remedies for neuropathic pain?
Yes. Some people benefit from acupuncture, omega-3 supplements, or mindfulness practices, but these should complement medical treatment not replace it.
Conclusion
Neuropathic pain is a complex and often chronic condition that can deeply affect physical and emotional well-being. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is the first step toward effective management. With proper diagnosis, a combination of medications, therapies, and lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve comfort and quality of life.
For those seeking personalized care and advanced pain management solutions, Aurora Compounding Pharmacy offers customized medication formulations designed to target neuropathic pain effectively. Their patient centred approach ensures every treatment is tailored to individual needs helping you live a healthier, pain-free life.