Scabies is a skin condition that can turn life into an itchy nightmare. Caused by tiny mites burrowing into the skin, it brings relentless itching, redness, and discomfort. If you’ve been diagnosed with scabies or suspect you have it, you may have come across Ivermectin 12 mg tablets as a potential treatment. But how exactly does this medication work, and what’s the correct dosage to rid yourself of this pesky problem?
Understanding Scabies and Why It’s So Troublesome
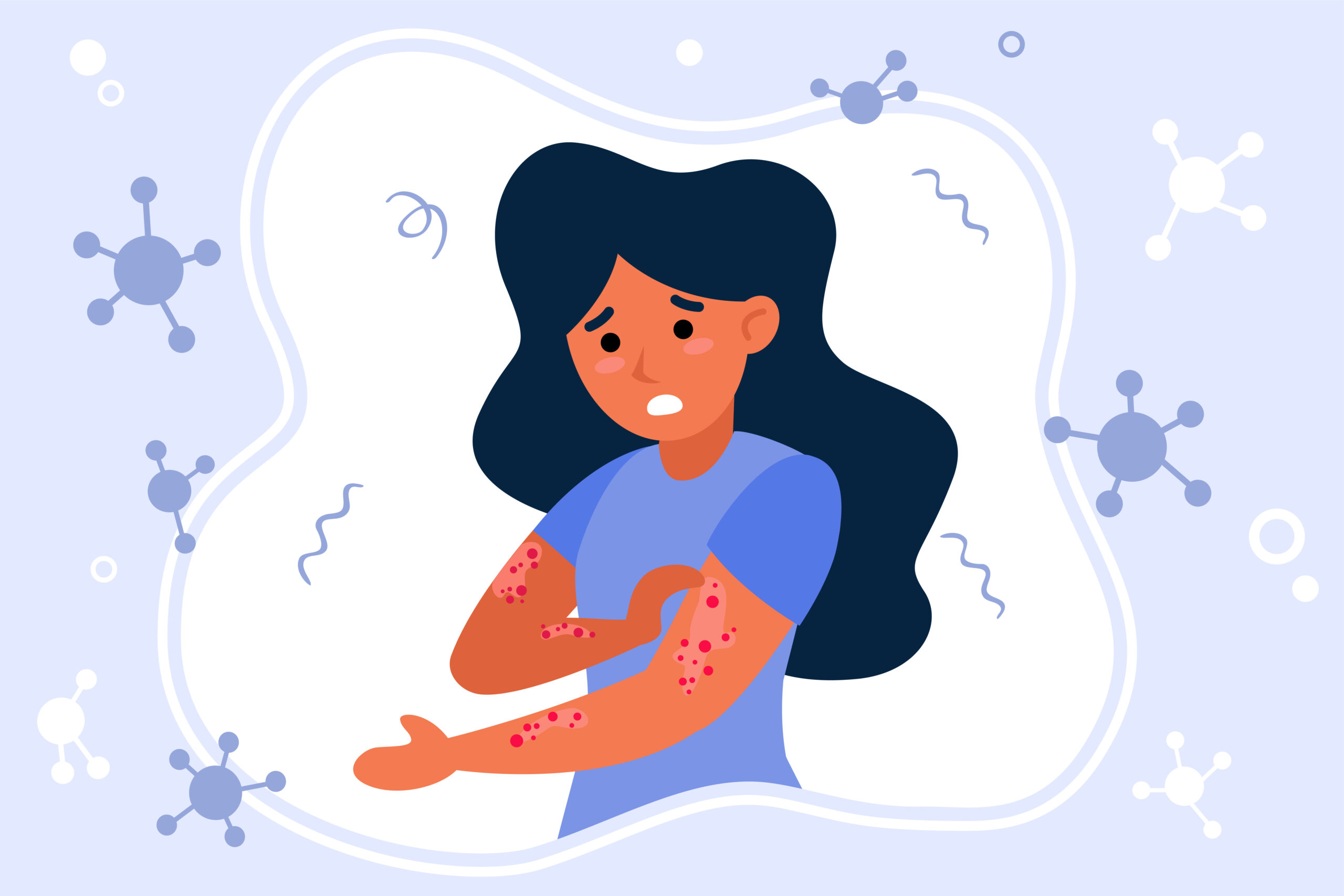
Scabies isn’t just any skin irritation. It’s caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, which digs into your skin to lay eggs. These mites are microscopic, but their effects are far from it. The intense itching they cause, particularly at night, can lead to sleepless nights and constant discomfort. If left untreated, scabies can spread rapidly across the body and even infect others.
What Is Ivermectin, and How Does It Work?
Ivermectin is an antiparasitic medication that has been used for decades to treat various parasitic infections, including scabies. It’s especially effective because it doesn’t just address the symptoms; it targets the root cause—those pesky mites.
When you take Iverheal 12, it works by paralyzing and killing the mites. This leads to the eventual clearing of the infestation from your skin. While topical treatments are also available for scabies, Ivermectin offers a convenient oral option, especially in severe or widespread cases.
Proper Dosage of Ivermectin 12 mg for Scabies
Now, let’s talk dosage. For scabies, the typical dose of Ivermectin is 200 micrograms per kilogram of body weight. However, a common and simplify approach is to prescribe a single dose of 12 mg, which is effective for most adults. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
- Initial Dose: You’ll take one Ivermectin 12 mg tablet. This dose is usually sufficient to kill most of the mites.
- Follow-Up Dose: In some cases, a second dose is recommended 7 to 14 days after the initial dose to ensure that any newly hatch mites are also eradicate. This follow-up dose is crucial because while Ivermectin kills adult mites, it may not completely kill all the eggs.
- Severe Cases: In severe cases of scabies, or when there are crust scabies (Norwegian scabies), higher doses or multiple treatments may be necessary under a doctor’s supervision.
Why It’s Important to Follow the Dosage Exactly
It’s tempting to skip the second dose once the itching subsides, but this can lead to a resurgence of the infestation. Remember, those mites are stubborn. Following the exact dosage and timing is essential for completely clearing scabies from your body.
What to Expect After Taking Ivermectin
After taking Ivermectin, you might notice some itching relief within a few days. However, don’t be alarm if the itching persists for a little while longer. This is a common reaction and doesn’t necessarily mean the treatment isn’t working. Your body might still be reacting to the dead mites.
It’s also crucial to wash your bedding, clothing, and towels thoroughly to prevent reinfestation. Scabies mites can survive on these items, so cleaning them helps to ensure you don’t get re-infected.
Are There Any Side Effects?
Like all medications, Ivermectin can have side effects, although they are generally mild. Common side effects include dizziness, nausea, or diarrhea. If you experience severe side effects or signs of an allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing or swelling, seek medical attention immediately.
Wrapping Up
Scabies can be a challenging condition to deal with, but Ivermectin 12 mg tablets offer an effective solution. By following the proper dosage and treatment plan, you can rid yourself of these mites and get back to a comfortable, itch-free life. Remember, the key to success with Ivermectin is following the dosage instructions closely and not skipping that crucial second dose.
If you think you have scabies or have been prescribe Ivermectin, don’t delay treatment. The sooner you take action, the sooner you’ll be on your way to recovery.