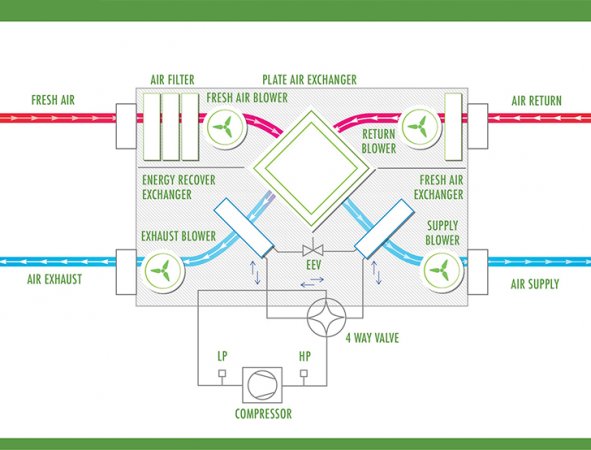
settings. They operate by transferring heat between two or more fluids without allowing them to mix, thus maintaining energy efficiency. Heat exchangers are integral to various heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, including HRV heat exchanger units designed to recover and reuse heat from exhausted air. These systems enhance indoor comfort and contribute to significant energy savings. By effectively regulating indoor temperatures and air quality, heat exchangers support healthier living environments while reducing the overall energy footprint of homes.
The Function of an HRV Heat-Exchanger
HRV systems continuously ventilate indoor spaces and recover heat from exhausted air. This process involves drawing in outdoor air, which is then filtered and preheated by the warm air being expelled from indoors. The HRV heat-exchanger’s core facilitates heat transfer between these air streams without mixing them. This heat recovery process allows the system to retain up to 90% of the energy that would otherwise be lost, significantly reducing heating demands.
HRV systems also help maintain consistent indoor temperatures and improve air quality by expelling stale air and introducing fresh air, contributing to a healthier and more energy-efficient home environment.
Home Air Heat Exchanger Applications
Home air heat-exchangers are widely utilised in various residential applications to enhance indoor climate control and energy efficiency. These systems are particularly beneficial in regions with significant temperature variations, where maintaining a comfortable indoor environment can be challenging. They are often integrated into HVAC systems to provide a continuous flow of tempered air, reducing the need for additional heating or cooling.
By transferring heat between the incoming and outgoing air streams, home air heat exchanger help maintain a consistent indoor temperature, which is essential for comfort and energy savings. Additionally, these systems can be installed in new builds or retrofitted into existing homes, making them a versatile solution for improving energy efficiency across different residential properties.
In homes with poor ventilation, air-heat exchangers can significantly improve indoor air quality by introducing fresh air and expelling stale air. This exchange process helps to reduce indoor pollutants, moisture levels, and odours, contributing to a healthier living environment. Advanced models may also feature adjustable settings to accommodate seasonal changes and varying household needs, enhancing their practicality and efficiency. Proper installation and maintenance of these systems ensure optimal performance and longevity, providing long-term benefits for homeowners.
Understanding the Air Heat Exchanger
Air-heat exchangers have several key components, including a heat exchange core, fans, filters, and ductwork. These elements work together to ensure efficient heat transfer and indoor air quality. The design of air-heat exchangers can vary, with common types including cross-flow, counter-flow, and rotary exchangers. Each type has unique advantages and applications, making selecting the appropriate model based on specific ventilation and energy-saving needs essential. The heat exchange core is typically made of materials with high thermal conductivity to maximise heat transfer.
Fans are crucial for driving air through the system, while filters help to remove contaminants from the air. Proper ductwork ensures smooth airflow between indoor and outdoor environments. Additionally, advanced models may incorporate variable speed controls and humidity sensors to optimise performance. Professionals should install air heat exchanger to ensure they are integrated seamlessly with existing HVAC systems.
This ensures optimal performance, energy efficiency, and longevity of the system. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspecting components, is necessary to keep the system operating at peak efficiency and to avoid any potential issues that could compromise its functionality.
Maintenance of Air-Heat Exchangers
Regular maintenance of air-heat exchangers is crucial to ensure efficient operation and extend their lifespan. Proper upkeep helps maintain optimal airflow, prevents mechanical failures, and ensures consistent performance. Below are key maintenance tasks that should be performed routinely.
Cleaning and Replacing Filters
Filters play a vital role in trapping dust and airborne particles, preventing them from entering the heat exchanger. Over time, these filters can become clogged, restricting airflow and reducing efficiency. Regular cleaning or replacement of filters ensures smooth operation and improves indoor air quality.
Inspecting Fans and Ductwork
Fans and ductwork should be checked for blockages, wear, or damage that could hinder airflow. Dust buildup or obstructions can strain the system, leading to higher energy consumption. Routine inspections help identify issues early, preventing costly repairs.
Monitoring for Unusual Noises or Vibrations
Strange sounds or vibrations often indicate mechanical problems, such as loose components or motor issues. Addressing these signs promptly can prevent further damage and ensure the system runs smoothly.
Lubricating Moving Parts
Fan motors and other moving parts require proper lubrication to minimize friction and wear. Regular lubrication reduces energy consumption and prolongs the lifespan of critical components.
Checking the Heat Exchange Core
Dust and debris can accumulate on the heat exchange core, reducing efficiency. Periodic inspection and cleaning ensure optimal heat transfer and maintain the system’s performance.
Air To Air Heat Exchanger Residential Use
Air-to-air-heat exchangers serve a vital function in residential environments by optimising indoor air quality and energy efficiency. These systems facilitate heat transfer between outgoing and incoming air streams, maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature without excessive energy consumption. The design of air-to-air-heat exchangers includes components like heat exchange cores, fans, and filters, which work together to achieve efficient heat transfer and air filtration.
Several factors must be considered when installing air-to-air-heat exchangers in homes. Proper sizing of the system is crucial to ensure it meets the ventilation needs of the specific household. Placement is also important; the system should be installed in a location that allows for optimal air circulation and easy access for maintenance. Integration with existing HVAC systems is essential for seamless operation, ensuring the heat exchanger works with other home heating and cooling components.
Advanced models may offer additional features, such as variable speed controls and humidity sensors, further enhancing their performance and adaptability to varying environmental conditions. By investing in a well-designed and correctly installed air to air heat exchanger residential, households can significantly improve their indoor environment while reducing energy costs.
Energy Efficiency and Air To Air Heat Exchangers
Air-to-airheat exchangers substantially reduce energy consumption in residential settings by recovering heat from expelled air and transferring it to incoming fresh air. This method reduces the workload on heating systems, conserving energy and cutting utility expenses. These systems are engineered to optimise energy recovery by using highly conductive materials in their heat exchange cores, which maximises heat transfer efficiency.
Beyond financial savings, air-to-air-heat exchangers also align with environmentally sustainable practices. By decreasing the reliance on heating systems, these units contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, supporting global efforts to combat climate change. The efficient operation of air-to-airair-to-air-heat exchangers is often enhanced by features such as variable-speed fans and advanced controls, which adjust performance based on real-time conditions.
An air to air heat exchanger in a home’s HVAC system provides continuous preheated airflow, lessening the demand for additional heating sources. These systems’ energy-saving potential is especially beneficial in regions with extreme weather conditions, where maintaining indoor comfort typically requires substantial energy expenditure. Consequently, air-to-air-heat exchangers are critical for achieving energy-efficient and environmentally responsible residential ventilation.
Heat Transfer Process in HRV Systems
The heat transfer process within HRV systems is fundamental to their operation. It relies on transferring thermal energy from one air stream to another without the two streams mixing. The warm, stale air is expelled from the indoor environment and passes through the heat exchanger core. Simultaneously, fresh, cooler air is drawn from outside and flows through the opposite side of the core. The heat exchanger core, typically constructed from materials with high thermal conductivity, facilitates heat transfer from the outgoing air to the incoming air. This preheats the fresh air before it enters the living spaces, ensuring minimal heat loss.
The continuous air movement through this system ensures that homes remain well-ventilated and energy-efficient, as most heat that would otherwise escape is retained and reused. This method conserves energy and helps maintain a consistent and comfortable indoor temperature throughout the year. Advanced HRV systems may include additional features like humidity control to enhance indoor air quality and comfort.
Ventilation and Indoor Air Quality
Proper ventilation is essential for indoor air quality and a healthy living environment. HRV systems play a crucial role by exchanging indoor air with fresh outdoor air while recovering heat. This process effectively removes indoor air pollutants, such as dust, pollen, and volatile organic compounds, which can adversely affect health. Additionally, these systems help manage indoor humidity levels, preventing problems like condensation and mould growth. By integrating HRV heat-exchangers, homes benefit from a consistent supply of fresh air without significant energy loss.
The overall result is a more comfortable and healthier indoor atmosphere, particularly important in modern, energy-efficient homes where airtight construction can limit natural ventilation. Advanced HRV systems may also feature enhanced filtration and humidity control to improve air quality and comfort. Regular maintenance ensures they operate effectively, providing ongoing benefits for indoor air quality and overall well-being.
Conclusion
HRV heat-exchangers are a crucial component of energy-efficient ventilation systems, providing a sustainable solution to maintaining air quality while minimizing energy consumption. By transferring heat from outgoing stale air to incoming fresh air, these systems ensure that homes and buildings stay comfortable year-round without wasting energy. HRV technology balances indoor air quality with energy efficiency, making it an ideal choice for eco-conscious homeowners and businesses. Investing in an HRV heat exchanger supports a healthier living environment and contributes to long-term energy savings.
FAQ’s
What is an HRV heat exchanger?
An HRV heat exchanger is designed to improve ventilation and energy efficiency by transferring heat between the outgoing stale air and incoming fresh air. It ensures proper air circulation without losing heat, which helps to maintain a comfortable indoor environment while reducing energy consumption.
How does an HRV heat-exchanger improve energy efficiency?
HRV heat-exchangers recover heat from the stale air expelled from the building and use it to pre-warm the incoming fresh air. This process reduces the need for additional heating or cooling, lowering energy costs and the overall demand for HVAC systems.
Can an HRV heat-exchanger be installed in any building?
HRV systems can be installed in various buildings, including homes, offices, and commercial properties. They are particularly beneficial in airtight, energy-efficient buildings where proper ventilation is crucial, but traditional ventilation systems may lead to energy loss.
Do HRV heat-exchangers require regular maintenance?
Yes, HRV systems need regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. This includes cleaning the filters, checking the ducts for blockages, and ensuring the heat exchanger core is debris-free. Regular maintenance can extend the system’s lifespan and maintain energy efficiency.
Are there any downsides to HRV heat-exchangers?
While HRV systems are highly effective, they may not suit extremely hot or humid climates as they can transfer moisture and heat. An ERV (Energy Recovery Ventilator) system might be a better option in such conditions as it also controls humidity.
| Related Business Listings |
| Contact Directory |
| Local Business Profiles |