Proper ventilation is crucial for maintaining a healthy and comfortable home environment. Without adequate ventilation, indoor air quality can suffer, leading to various health issues. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of house ventilation, different types of ventilation systems, how to assess your home’s ventilation needs, natural and mechanical ventilation techniques, tips for improving indoor air quality, and more. By the end of this post, you will better understand how ventilation plays a vital role in your home.
Understanding the Importance of Proper Ventilation
Ventilation is not just a luxury; it’s a necessity for a healthy living space. Its role extends beyond simply refreshing the air; it serves as a critical component in maintaining the well-being of your home’s occupants. One of the primary benefits of effective ventilation is its ability to dilute and eliminate harmful pollutants. These pollutants range from volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by paints, furnishings, and cleaning products to allergens such as pollen and pet dander. Without a proper escape route, these substances can accumulate to levels that pose health risks, particularly exacerbating conditions such as asthma and allergies.
Moreover, ventilation plays a pivotal role in moisture control. Excessive humidity can create an ideal environment for mould and mildew to thrive, not to mention the potential structural damage to your home through wood rot and paint deterioration. By regulating the moisture levels in your indoor environment, you safeguard your health and protect the integrity of your home’s structure and finishes.
Additionally, adequate ventilation is crucial for preventing the buildup of indoor pollutants resulting from everyday activities such as cooking, bathing, and breathing. Carbon dioxide levels, for example, can rise to unhealthy levels in poorly ventilated spaces, leading to reduced cognitive function and discomfort.
Understanding these aspects makes it clear that proper ventilation is not merely about ensuring a constant supply of fresh air. It’s about creating a living environment that supports health, comfort, and the longevity of your home.
Different Types of Ventilation Systems
When exploring ventilation options, it’s important to understand the systems available, each designed to suit various home environments and preferences. Broadly, ventilation systems are categorized into natural, mechanical, and hybrid.
Natural ventilation relies on passive airflow through doors, windows, and vents, utilizing the natural forces of wind and buoyancy to move air in and out of the home. This method is cost-effective and environmentally friendly but may not be reliable in all climates or seasons.
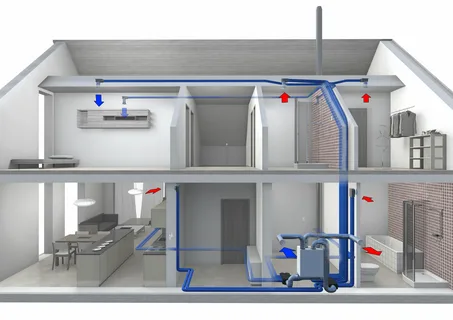
On the other hand, mechanical ventilation uses fans and duct systems to remove stale indoor air and supply fresh outdoor air. This category can be subdivided further into exhaust, supply, balanced, and energy recovery systems. Exhaust ventilation systems depress the home, pulling outside air through windows and vents while expelling indoor air. Supply systems operate oppositely by pressurizing the home, pushing air in and forcing stale air out through designed openings. Balanced systems combine supply and exhaust functions to maintain controlled air exchange without pressure or depressurizing the home. Lastly, energy recovery ventilation (ERV) and heat recovery ventilation (HRV) are sophisticated forms of balanced systems that recover heat (and sometimes humidity) from exchanged air, making them highly efficient, especially in extreme climates.
Hybrid ventilation systems incorporate natural and mechanical elements, optimizing energy efficiency while ensuring consistent air quality regardless of external conditions. This approach is increasingly popular in modern homes seeking a balance between environmental impact and indoor air comfort.
Each system offers unique benefits and considerations, making evaluating your home’s specific needs, climate, and structural possibilities crucial before deciding on the best ventilation strategy.
How to Assess Your Home’s Ventilation Needs
Assessing your home’s ventilation needs is critical to ensure your living space is comfortable and healthy. Here are four key factors to consider:
Evaluate Indoor Air Quality
Begin by evaluating your indoor air quality. Signs of poor ventilation include persistent odours, condensation on windows, and increased health issues such as allergies or respiratory problems. Air quality monitors can measure levels of pollutants and humidity, providing a clearer picture of your home’s air quality.
Consider Home Layout and Size
Your home’s layout and size play significant roles in its ventilation needs. Larger homes may require more sophisticated systems, like balanced or hybrid ventilation, to effectively manage air quality. Room design and placement can also impact natural ventilation efficiency, necessitating a tailored approach to ensure adequate airflow.
Identify Existing Ventilation Systems
Review any existing ventilation systems in your home, such as exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens or air intakes for heating and cooling systems. Determine whether these are sufficient for your needs or if additional or upgraded systems are required to improve air exchange and control humidity levels.
Understand Local Climate Conditions
Climate greatly influences your home’s ventilation needs. Homes in humid climates may need enhanced moisture control, while those in colder regions might benefit from heat recovery ventilation systems to minimize energy loss. Assessing how your local climate affects your home will guide you in selecting the most appropriate ventilation strategy.
By carefully considering these factors, you can effectively assess your home’s ventilation needs and make informed decisions to enhance indoor air quality and comfort.
Natural & Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and Best Practices
Exploring the synergy between natural and mechanical ventilation offers a comprehensive approach to maintaining optimal indoor air quality. Natural ventilation strategies leverage the home’s design and its occupants’ behaviours. Opening windows and doors to create a cross breeze can significantly refresh the indoor environment. Consider strategic window placement or the addition of operable skylights to enhance this effect, especially in areas where natural breezes are common. Remember, the effectiveness of natural ventilation is greatly influenced by the home’s orientation, window types, and external landscaping.
On the mechanical side, incorporating energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) or heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) can provide controlled and efficient ventilation. These systems are particularly useful in extreme climates, where opening windows might not be practical. They exchange indoor and outdoor air while conserving energy from the outgoing air to precondition the incoming air. Installing exhaust fans in high-moisture areas such as bathrooms and kitchens also helps remove contaminants directly from their source, preventing their spread throughout the home.
The best practices for integrating natural and mechanical ventilation involve a holistic view of your home’s airflow. This includes considering the natural pathways air might follow through your home and how mechanical systems can complement these paths. For instance, ensuring that mechanical ventilation does not undermine natural airflows but works in concert with them can maximize energy efficiency and air quality. Additionally, regular maintenance of mechanical systems, including filter replacement and duct cleaning, ensures these systems operate effectively and contribute positively to your home’s overall ventilation strategy.
Improving Indoor Air Quality with House Ventilation
Improving indoor air quality through house ventilation involves a strategic blend of reducing indoor pollutants and enhancing fresh air flow. Start by targeting sources of indoor pollution:
- Ensure that combustion appliances are properly vented outdoors.
- Use low-VOC materials in your home renovation projects.
- Minimize using air fresheners and candles that can release harmful chemicals.
Regularly cleaning and vacuuming can reduce dust, pet dander, and other particulates that compromise air quality.
Additionally, paying attention to your home’s humidity levels is crucial. High humidity can encourage the growth of mould and dust mites, whereas too low humidity can cause respiratory problems and discomfort. Dehumidifiers or humidifiers should be used to maintain healthy levels, ideally between 30% and 50%.
Incorporating plants into your home decor adds a touch of nature and can contribute to better air quality. Certain plants have been known to absorb pollutants, although this should be seen as complementary to, not a replacement for, good ventilation practices.
Finally, engage your home’s mechanical ventilation systems efficiently. Use exhaust fans during and after activities introducing moisture or pollutants, such as cooking and showering. If your home is equipped with an ERV or HRV system, ensure it’s properly set to balance the indoor climate without overburdening energy consumption. Through these targeted actions, homeowners can significantly enhance the air quality in their living spaces, making them healthier and more pleasant environments.
Ventilation Tips for Different Rooms in Your Home
Living Room and Common Areas
Maximize natural ventilation in these spaces by regularly opening windows to allow for a cross-breeze, especially during cooler parts of the day. If your home is equipped with ceiling fans, use them with open windows to enhance air circulation. Consider installing trickle vents to continuously introduce fresh air without significant heat loss.
Kitchen
An exhaust fan is indispensable, Given the kitchen’s propensity for moisture and odours. Ensure it vents directly outside to efficiently remove cooking fumes and excess humidity. Open a window while cooking to aid in the ventilation process. For open-plan living areas, consider a range hood with a higher capacity to manage air quality effectively.
Bathroom
Like the kitchen, an exhaust fan is crucial in bathrooms to expel moist air and prevent mould growth. Use the fan during and for about 20 minutes after showers to maximize moisture removal. A small operable window can provide additional ventilation and natural light if privacy allows.
Bedroom
Good air quality is essential for a restful sleep. If outdoor noise levels permit, leave windows slightly open overnight to ensure a steady supply of fresh air. For bedrooms on upper floors, consider installing operable skylights to take advantage of cooler night air and the stack effect for natural ventilation.
Energy Efficiency and Ventilation: Finding the Balance
Achieving harmony between ventilation and energy efficiency is paramount in modern homes. Optimal ventilation strategies ensure fresh air supply and pollutant removal without compromising energy savings. Key to this balance is energy recovery ventilation (ERV) systems and heat recovery ventilation (HRV) systems, which precondition incoming air using energy from the outgoing air, thus significantly reducing the energy required to heat or cool the house. Incorporating such systems, alongside mindful practices like sealing leaks and adding insulation, can drastically reduce energy waste. Additionally, using smart natural ventilation during favourable weather conditions can further reduce reliance on mechanical systems, conserving energy. Employing programmable thermostats allows for precise control over ventilation systems, ensuring they operate only when necessary. This integrated approach maintains indoor air quality and aligns with energy conservation goals, demonstrating that with thoughtful planning and technology, it’s possible to enjoy fresh indoor air while also being mindful of energy consumption.
Conclusion
The significance of effective house ventilation within the home cannot be overstated. It’s the cornerstone of creating an environment that is not just comfortable to live in but also promotes the well-being of everyone under its roof. From diluting indoor pollutants to managing moisture and enhancing the overall air quality, the role of proper ventilation is multifaceted. We’ve explored the various systems available, from natural to mechanical and even hybrid solutions, each catering to different needs and preferences. Assessing your home’s requirements is a critical first step, followed by integrating the right combination of techniques to foster a healthy indoor atmosphere.
FAQs
Q: How often should I assess my home’s ventilation needs?
A: It’s recommended to assess your home’s ventilation needs annually, as changes in your living situation, home improvements, or varying environmental conditions can affect your needs.
Q: Can plants improve indoor air quality?
A: While plants can absorb certain pollutants, they are more complementary to a well-ventilated home rather than a standalone solution. It’s best to rely on adequate ventilation for significant air quality improvements.
Q: Is it possible to have too much house ventilation in my home?
A: Excessive ventilation can lead to energy loss, discomfort due to drafts, and, in some cases, too low humidity levels. Finding a balance that suits your home’s needs and climate conditions is important.