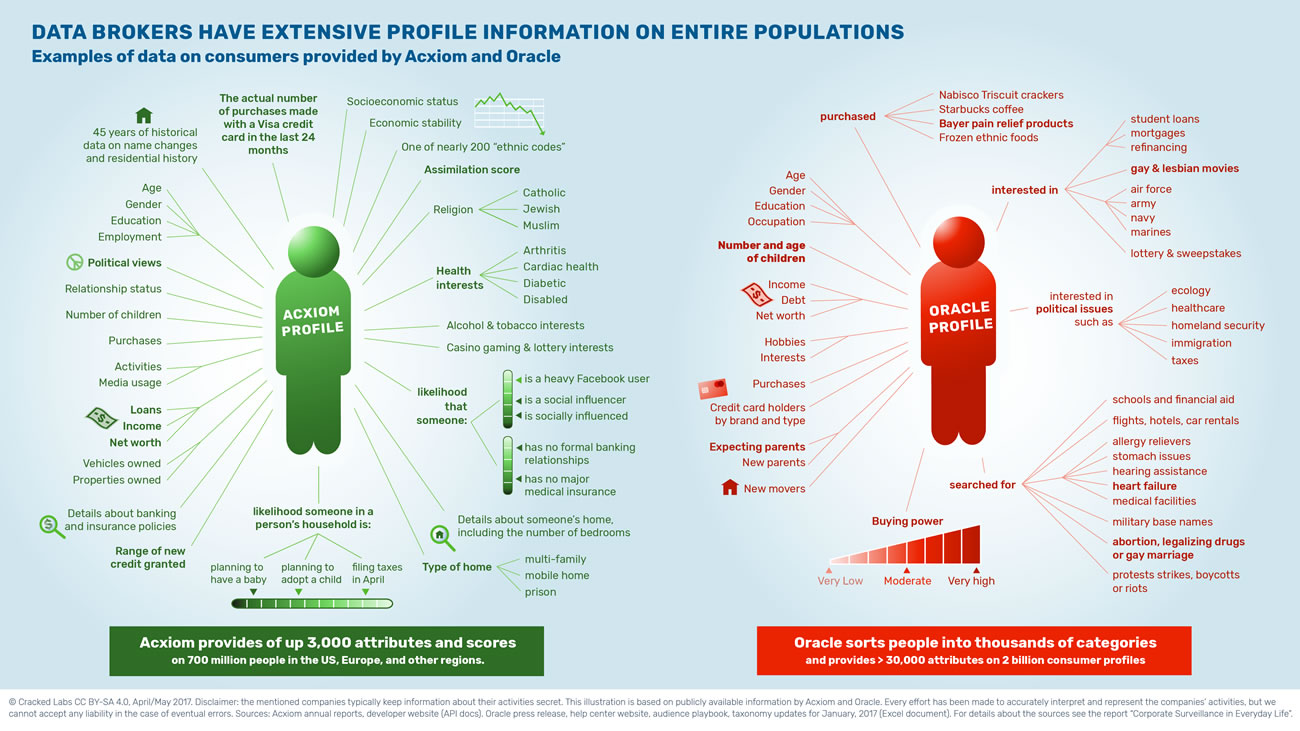
In today’s interconnected world, the seamless flow of information is paramount. This section delves into the intricate mechanisms that facilitate the delivery of customized services within the digital realm. We explore how entities collect and analyze vast amounts of information to enhance user experiences and optimize service offerings. This exploration is crucial for understanding the dynamics of modern communication networks and the role of specialized intermediaries in shaping these experiences.
Key Players and Their Roles
At the heart of this discussion are entities that aggregate and process consumer data to tailor services more effectively. These intermediaries play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between raw data and actionable insights. By examining their methodologies and ethical considerations, we gain a deeper understanding of how personalized services are crafted and delivered to consumers. This analysis not only highlights the technological advancements but also underscores the importance of privacy and consent in the digital age.
Impact on Consumer Experience
The evolution of personalized services has significantly impacted consumer interactions with digital platforms. Through advanced analytics and data-driven strategies, these services aim to meet individual needs more precisely. This section will discuss the benefits and challenges associated with such personalized approaches, emphasizing the balance between innovation and user privacy. As we navigate through these complexities, it becomes evident that transparency and ethical data practices are essential for sustainable growth in the digital marketplace.
In conclusion, this section provides a comprehensive overview of how information intermediaries contribute to the customization of services in the digital communication sector. By focusing on the interplay between data utilization, technological innovation, and consumer rights, we aim to equip readers with a nuanced understanding of this critical aspect of modern digital life.
Understanding Data Brokers
This section delves into the pivotal role that information intermediaries play within the communication sector. It explores how these entities facilitate the exchange of valuable insights, which are crucial for enhancing service offerings and customer experiences.
Information intermediaries are key players in the communication sector, acting as conduits between vast amounts of user data and service providers. Their primary function involves collecting, analyzing, and selling detailed profiles of consumers, which can range from demographic details to usage patterns. This information is instrumental for service providers in tailoring their offerings to meet specific customer needs and preferences.
Moreover, these intermediaries help in optimizing network operations by providing insights into traffic patterns and consumer behavior. This enables service providers to allocate resources more efficiently, ensuring better service quality and reliability. Additionally, the insights derived from these intermediaries can lead to the development of innovative services that address emerging market demands.
In essence, information intermediaries not only enhance the operational efficiency of service providers but also contribute significantly to the evolution of the communication sector by enabling a more personalized and responsive service environment.
Role of Information Mediators in Telecom

This section delves into the significant influence of information mediators within the telecom sector. It explores how these entities facilitate the exchange of consumer information, impacting privacy and service customization.
Information mediators play a crucial role in the telecom sector by aggregating and analyzing vast amounts of consumer data. This data is then used to enhance service offerings and target marketing efforts more effectively. However, this process raises several privacy concerns that need to be addressed.
- Collection of Sensitive Information: Information mediators often collect highly sensitive data, including personal identifiers, browsing habits, and even location data. This extensive collection can lead to privacy breaches if not managed securely.
- Lack of Transparency: Many consumers are unaware of how their information is being used by telecom companies through information mediators. This lack of transparency can lead to mistrust and opt out whitepages dissatisfaction.
- Potential for Misuse: The data gathered can be misused if not properly regulated. This includes unauthorized selling of information to third parties or using it for purposes other than those agreed upon by the consumer.
Addressing these concerns is essential for maintaining consumer trust and ensuring ethical practices within the telecom sector. Regulatory frameworks and consumer protections must evolve to keep pace with the technological advancements and the growing complexity of data management.
Data Privacy Concerns
In today’s digital age, the collection and utilization of personal information by various entities have raised significant concerns regarding privacy. This section delves into the implications of such practices on individuals and the measures needed to safeguard their personal data.
The extensive gathering of personal information by service providers can lead to a range of privacy issues. Consumers often find themselves unaware of how their details are being used, who has access to this information, and the potential risks associated with its dissemination. These concerns are particularly pertinent in sectors where personal data is routinely collected and analyzed to tailor services to user preferences.
One major issue is the potential for misuse of personal information. Without stringent controls and transparent policies, there is a risk that sensitive data could be exploited for purposes beyond the original intent, such as targeted marketing or even fraudulent activities. This not only infringes on individual privacy but also erodes trust in the service providers handling such information.
Moreover, the lack of control over personal data can lead to a sense of vulnerability among consumers. The ability to monitor and manage how personal information is used is crucial for maintaining privacy. However, many consumers feel they have little say in this process, which can lead to dissatisfaction and a reluctance to engage with services that require extensive data collection.
Addressing these concerns requires a multifaceted approach. Enhancing transparency about data usage, providing clear options for consumers to opt-in or out of data collection, and implementing robust security measures are essential steps. Additionally, regulatory frameworks must evolve to keep pace with technological advancements and ensure that privacy protections are up to date and effectively enforced.
In conclusion, while the use of personal information can offer benefits in terms of customized services, it must be balanced with strong privacy protections. Ensuring that consumers are informed and have control over their data is not only a matter of ethical practice but also a critical component of building and maintaining trust in digital services.
Impact on Consumer Plans
This section delves into how the practices of information aggregators and their interactions with communication service providers influence the offerings and choices available to end-users. It explores the broader implications on individual plans, highlighting both the advantages and potential drawbacks for consumers.
Enhanced Personalization: One of the primary impacts is the increased personalization of service packages. By leveraging collected information, providers can tailor their offerings more closely to the specific needs and behaviors of consumers. This can lead to more efficient and satisfying service experiences, as plans are optimized based on usage patterns and preferences.
Price Variability: Another significant effect is the variability in pricing structures. With detailed insights into consumer behavior, service providers might adjust their pricing dynamically, potentially leading to both cost savings and increased expenses depending on usage and negotiation power. This dynamic pricing can be both a boon and a challenge for consumers, requiring careful monitoring and understanding of their own usage patterns.
Privacy Concerns: The collection and use of personal information also raise important privacy issues. Consumers may feel uncomfortable with the extent of information being gathered and used to shape their service plans. This concern underscores the need for robust privacy protections and transparent practices from service providers.
Choice Limitations: On the flip side, there is the potential for limiting consumer choices. As services become more tailored, the range of generic options might diminish, potentially restricting consumer freedom to choose services that do not fit neatly into predefined categories. This trend could lead to a more homogenized market, reducing the diversity of offerings.
In conclusion, while the integration of information from aggregators into service provision can lead to more personalized and potentially efficient services, it also poses challenges related to privacy and choice. Balancing these aspects is crucial for ensuring that consumer interests are adequately protected and promoted.
Regulatory Framework

Regulation plays a crucial role in governing the collection, use, and protection of information within the sector. This section delves into the legal structures that oversee these processes, ensuring transparency, fairness, and security for all stakeholders.
The regulatory framework is designed to balance the interests of service providers with the rights and expectations of consumers. It encompasses a range of laws and guidelines that dictate how personal information can be gathered, stored, and utilized. These regulations are essential to prevent misuse of sensitive information and to maintain public trust in digital services.
Key components of the regulatory framework include privacy laws, data protection acts, and industry-specific guidelines. These elements work together to create a comprehensive system that not only protects individual privacy but also promotes ethical practices among service providers. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory, and failure to adhere can result in significant penalties and damage to corporate reputation.
Moreover, the regulatory framework encourages innovation by setting clear boundaries within which companies can operate. This clarity helps in developing new services and technologies that respect user privacy and comply with legal standards. As technology evolves, so too does the regulatory landscape, with ongoing efforts to update and refine these frameworks to meet new challenges and protect consumer interests.
In conclusion, the regulatory framework is a vital component of the digital ecosystem, ensuring that while companies leverage information for growth and innovation, the rights and privacy of individuals are safeguarded. This balance is crucial for the sustainable development of the sector and for maintaining public confidence in digital technologies.
Techniques for Data Collection
This section delves into the methods employed by organizations to gather information that fuels their operational strategies and enhances customer experiences. Understanding these techniques is crucial for consumers and businesses alike, as it sheds light on how personal details are acquired and utilized.
Web Tracking and Analytics: One of the primary methods involves the use of cookies and similar technologies to monitor user activity online. This helps companies analyze browsing patterns, preferences, and behaviors, which can then be used to tailor services and advertisements.
Surveys and Feedback Forms: Another common approach is the direct collection of information through surveys and feedback forms. These tools allow companies to gather specific insights about customer satisfaction, needs, and expectations.
Social Media Monitoring: With the rise of social platforms, many organizations now monitor public posts and interactions on these sites. This not only provides real-time insights into consumer sentiments but also helps in identifying trends and potential issues.
Transactional Data Analysis: Detailed analysis of transactional records, such as purchases and subscriptions, offers a wealth of information about spending habits and service usage. This data is invaluable for optimizing product offerings and marketing strategies.
Location-Based Services: The use of GPS and other location-tracking technologies allows for the collection of data related to user movements and preferences based on geographical locations. This information can be particularly useful for businesses aiming to provide location-specific services or promotions.
In conclusion, the techniques for information collection are diverse and multifaceted, each serving specific purposes in enhancing business operations and customer interactions. As technology evolves, so too will these methods, continually reshaping the landscape of consumer engagement and business strategy.
Benefits for Telecom Companies
This section explores the advantages that communication service providers gain through strategic information management. By leveraging insights from collected details, these companies can enhance their operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
One of the primary benefits is the ability to tailor services more accurately to meet consumer needs. This customization not only improves customer loyalty but also increases revenue streams. Additionally, detailed analysis allows for better resource allocation, reducing operational costs and improving profitability.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Customization | Enhances customer satisfaction by offering services that align closely with individual preferences and usage patterns. |
| Revenue Growth | Increases income by targeting promotional offers and new services to segments that are most likely to benefit and subscribe. |
| Cost Reduction | Optimizes operational expenses through efficient resource management and by avoiding unnecessary expenditures. |
| Competitive Advantage | Gains a strategic edge by being able to respond quickly to market changes and customer demands. |
Furthermore, the insights gained from detailed analysis can lead to innovative service developments, keeping the company at the forefront of technological advancements and consumer trends. This proactive approach not only secures existing customer bases but also attracts new clientele, thereby expanding market share.
Challenges Facing Data Brokers
In this section, we delve into the multifaceted obstacles that information intermediaries encounter in their operational landscape. These challenges range from regulatory pressures to technological advancements, each posing unique hurdles to the efficient management and utilization of collected information.
Regulatory Compliance: One of the primary challenges is navigating the complex and ever-evolving regulatory environment. As governments worldwide implement stricter laws to protect consumer privacy, intermediaries must continually adapt their practices to ensure compliance. This includes understanding and implementing regulations such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California, which mandate stringent data protection standards.
Technological Advancements: The rapid pace of technological innovation also presents significant challenges. Intermediaries must stay ahead of the curve, adopting new technologies to enhance data security and efficiency. However, this requires substantial investment in research and development, as well as training for staff to handle advanced systems effectively.
Data Security: Ensuring the security of collected information is another critical challenge. With the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber-attacks, intermediaries face immense pressure to safeguard data against breaches. This involves implementing robust cybersecurity measures and regularly auditing their systems for vulnerabilities.
Public Perception: Building and maintaining public trust is crucial. Negative perceptions about data privacy can severely impact the reputation and operations of intermediaries. Therefore, transparent communication about data handling practices and demonstrating commitment to ethical data use is essential.
Economic Pressures: Lastly, economic factors play a significant role. The cost of compliance, technological upgrades, and maintaining high standards of data security can be substantial. Balancing these costs with the need to remain competitive in a saturated market is a delicate task.
In conclusion, while information intermediaries play a vital role in the digital economy, they must navigate a series of complex challenges to continue providing valuable services. Addressing these issues requires a strategic approach, combining technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and a strong commitment to ethical practices.
Future Trends in Data Management
Exploring the Evolution of Information Handling: As technology advances, the methods and strategies for managing sensitive information are undergoing significant transformations. This section delves into the emerging practices and innovations that are shaping the landscape of information governance, focusing on how these changes impact both businesses and end-users.
Enhanced Security Measures: One of the primary trends in information management is the escalation of security protocols. With increasing cyber threats, organizations are investing heavily in advanced encryption techniques and robust authentication systems to safeguard confidential details.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are playing pivotal roles in predictive analytics and automated decision-making processes. These technologies are not only enhancing the efficiency of information processing but also improving the accuracy of data-driven insights.
Focus on Transparency and User Control: There is a growing emphasis on transparency in how information is collected, used, and shared. This trend includes empowering users with greater control over their personal details, allowing them to dictate how their data is utilized.
Sustainable Data Practices: Environmental considerations are also influencing data management strategies. Companies are increasingly adopting sustainable practices in data storage and processing to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global sustainability efforts.
Regulatory Compliance and Adaptation: As regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, businesses must stay abreast of changes and adapt their information management practices accordingly. This includes complying with new privacy laws and international standards that protect user rights and data integrity.
Conclusion: The future of information management is characterized by a blend of technological innovation, heightened security, and a strong focus on user rights and environmental sustainability. As these trends continue to develop, they will undoubtedly reshape the way we handle and perceive sensitive information.
Consumer Rights and Protections

In the evolving landscape of information exchange, safeguarding the interests of end-users is paramount. This section delves into the essential rights and protections that consumers should be aware of, ensuring they are not only informed but also empowered in their interactions with service providers.
Firstly, transparency is a cornerstone of consumer rights. Users have the right to know what information is being collected about them, how it is being used, and with whom it is shared. This transparency not only builds trust but also allows consumers to make informed decisions about the services they use.
Secondly, the right to privacy is critical. Consumers should have control over their personal information, including the ability to opt-out of having their data collected or shared. This right extends to the protection of sensitive information, ensuring that it is not misused or exposed without consent.
Additionally, consumers have the right to fair treatment. This includes access to clear and understandable terms of service, as well as fair and reasonable pricing. Service providers must ensure that their practices do not discriminate against any group of users, and that all consumers have equal access to services and support.
Lastly, the right to recourse is essential. Consumers should have avenues to address grievances, including the ability to seek compensation for any damages incurred due to improper handling of their information. This includes access to legal remedies and regulatory bodies that can enforce consumer protections.
In conclusion, while the collection and use of information continue to evolve, the rights and protections of consumers must remain at the forefront. By advocating for these rights, we ensure a balanced and fair ecosystem where consumers are respected and protected.



